Controllable Artistic Text Style Transfer
via Shape-Matching GAN
 |
 |
 |
 |
| (a) source image | (b) adjustable stylistic degree of glyph | (c) stylized text | (d) application |
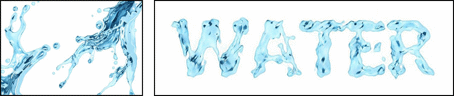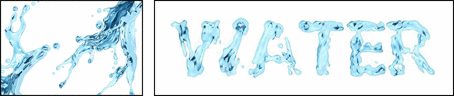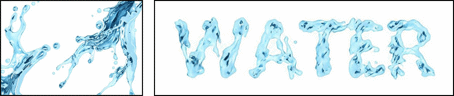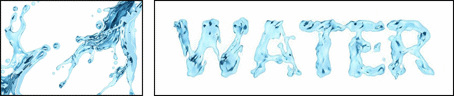 |
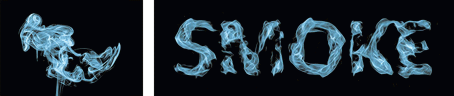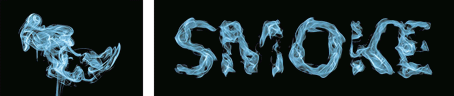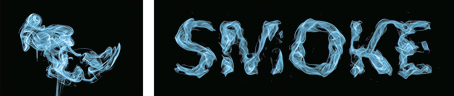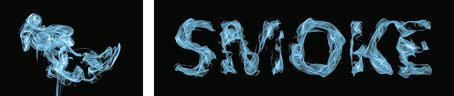 |
| (e) liquid artistic text rendering | (f) smoke artistic text rendering |
Figure 1. We propose a novel style transfer framework for rendering artistic text from a source style image in a scale-controllable manner. Our framework allows users to (b) adjust the stylistic degree of the glyph (i.e. deformation degree) in a continuous and real-time way, and therefore to (c) select the artistic text that is most ideal for both legibility and style consistency. The generated diverse artistic text will facilitate users to design (d) exquisite posters and (e)(f) dynamic typography.
Abstract
Artistic text style transfer is the task of migrating the style from a source image to the target text to create artistic typography. Recent style transfer methods have considered texture control to enhance usability. However, controlling the stylistic degree in terms of shape deformation remains an important open challenge. In this paper, we present the first text style transfer network that allows for real-time control of the crucial stylistic degree of the glyph through an adjustable parameter. Our key contribution is a novel bidirectional shape matching framework to establish an effective glyph-style mapping at various deformation levels without paired ground truth. Based on this idea, we propose a scale-controllable module to empower a single network to continuously characterize the multi-scale shape features of the style image and transfer these features to the target text. The proposed method demonstrates its superiority over previous state-of-the-arts in generating diverse, controllable and high-quality stylized text.
Framework
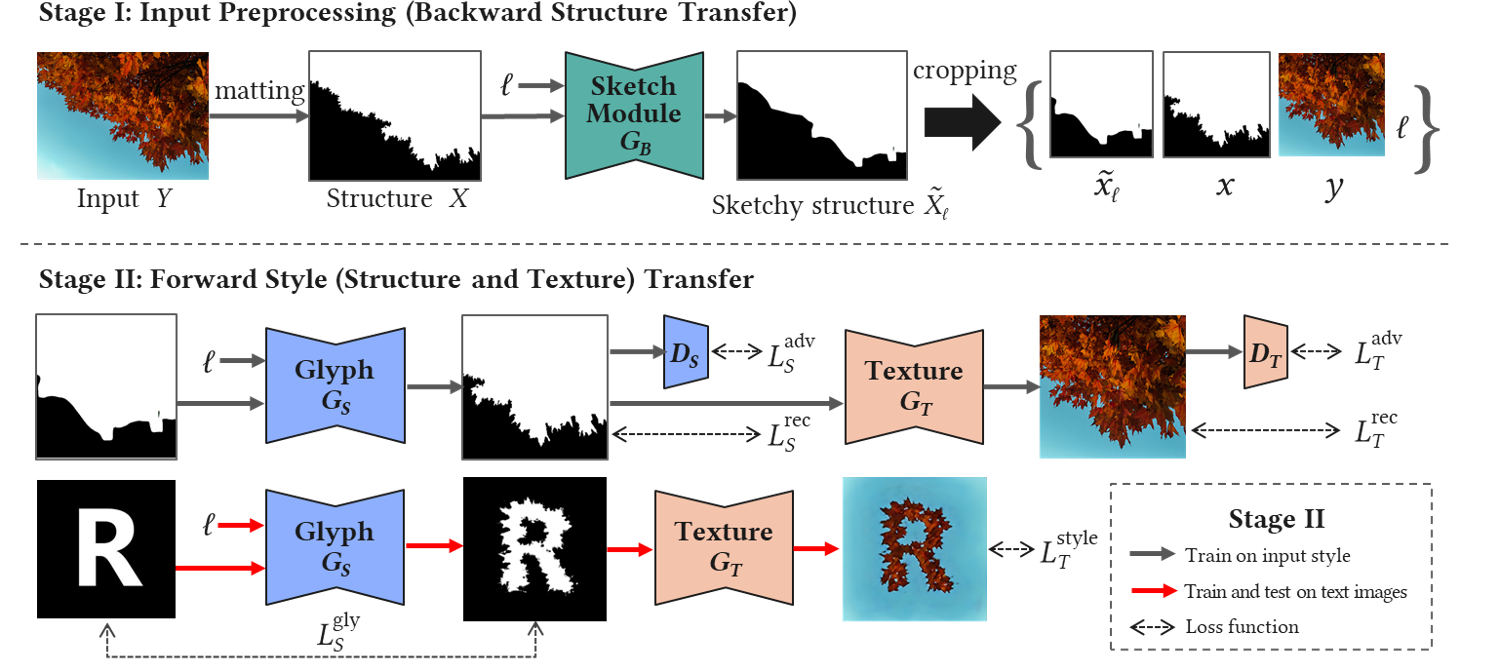
Figure 2. Overview of our bidirectional shape matching framework.
Resources
Citation
@inproceedings{Yang2019Controllable,
title={Controllable Artistic Text Style Transfer via Shape-Matching GAN},
author={Yang, Shuai and Wang, Zhangyang and Wang, Zhaowen and Xu, Ning
and Liu, Jiaying and Guo, Zongming},
booktitle={International Conference on Computer Vision},
year={2019}
}
Selected Results
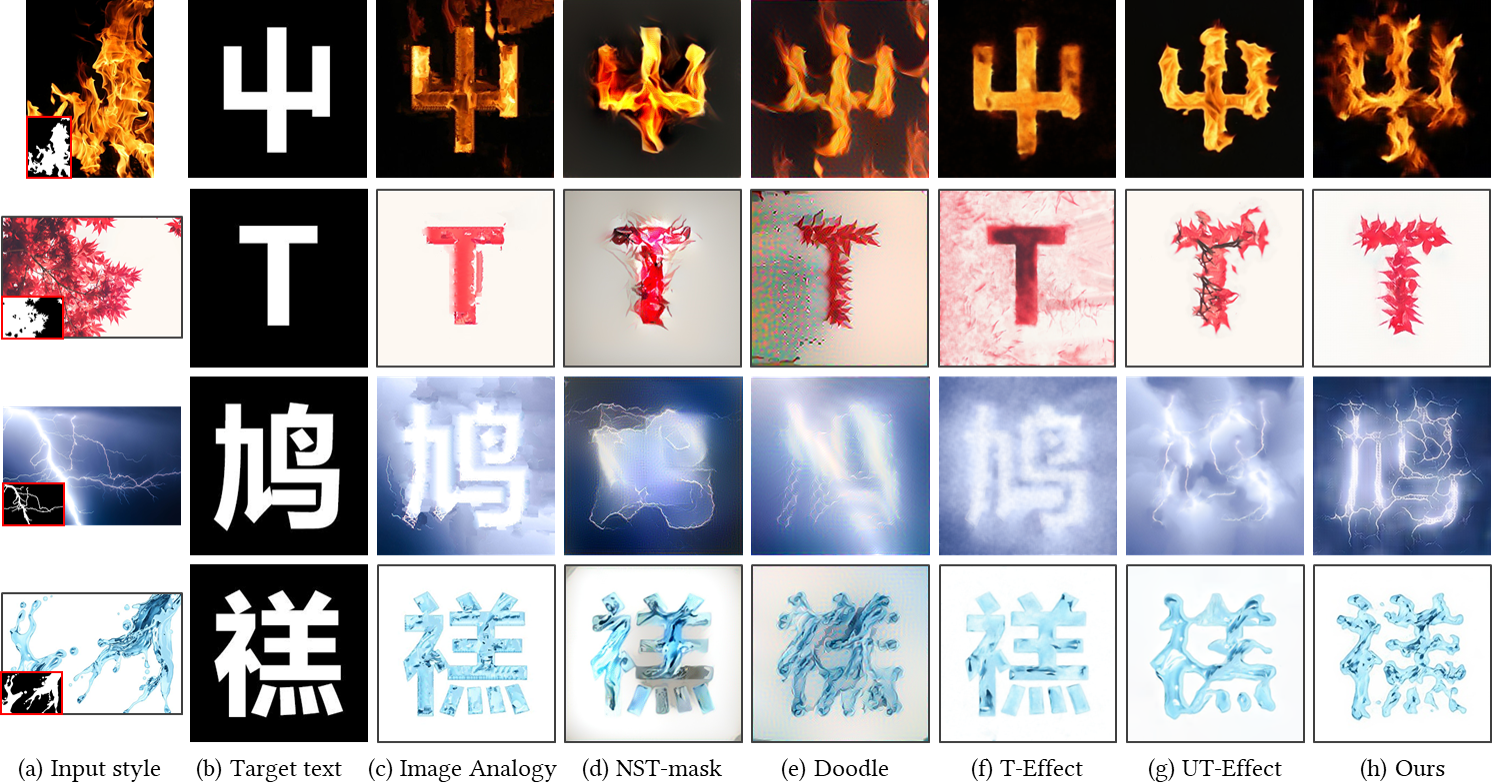

Figure 3. Comparison with state-of-the-art methods on various styles. (a) Input style with its structure map in the lower-left corner. (b) Target text. (c) Image Analogy [1]. (d) Neural Style Transfer [2] with spatial control [3]. (e) Neural Doodle [4]. (f) T-Effect [5]. (g) UT-Effect [6]. (h) Our style transfer results. We manually select the suitable deformation degrees for UT-Effect [6] and out method.
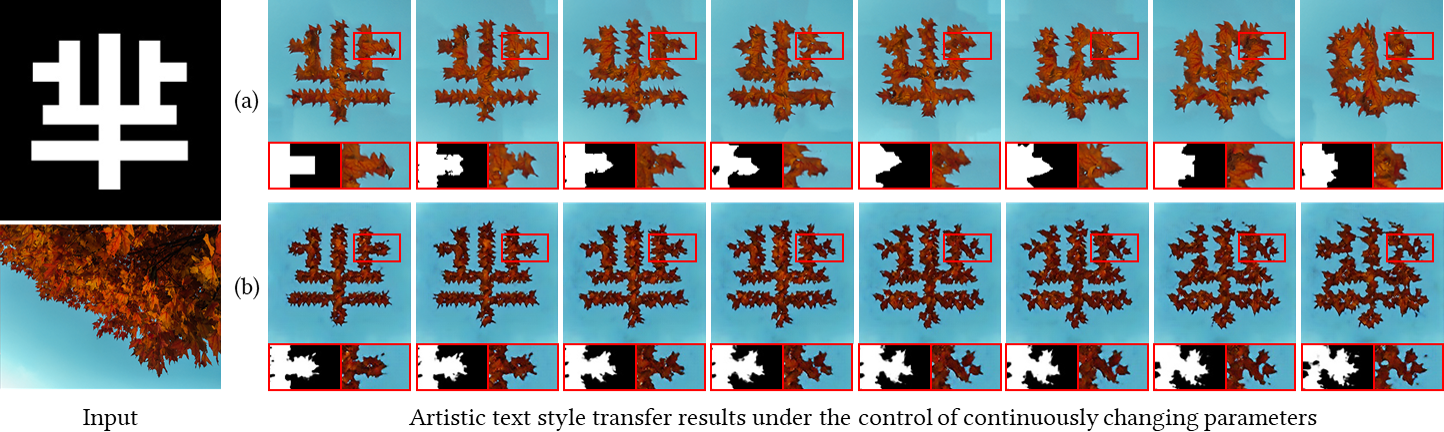

Figure 4. Qualitative comparison between the proposed method and other scale-controllable style transfer methods. For the first column, from top to bottom: the target text and style image. Remaining columns: Results by (a) UT-Effect [6] with resolution level evenly increasing from 1 to 7; (b) the proposed method with l evenly increasing from 0 to 1. All results are produced by one single model for each method. The red box region is shown enlarged in the bottom with the corresponding structure map provided for better visual comparison.
Reference
[1] A. Hertzmann, C. E. Jacobs, N. Oliver, B. Curless, and D. H. Salesin. Image analogies. SIGGRAPH 2001.
[2] L. A. Gatys, A. S. Ecker, and M. Bethge. Image style transfer using convolutional neural networks. CVPR 2016.
[3] L. A. Gatys, A. S. Ecker, M. Bethge, A. Hertzmann, and E. Shechtman. Controlling perceptual factors in neural style transfer. CVPR 2017.
[4] A. J. Champandard. Semantic style transfer and turning two-bit doodles into fine artworks. arXiv:1603.01768, 2016
[5] S. Yang, J. Liu, Z. Lian, and Z. Guo. Awesome typography: Statistics-based text effects transfer. CVPR 2017.
[6] S. Yang, J. Liu, W. Yang, and Z. Guo. Context-aware textbased binary image stylization and synthesis. TIP 2019.